☔ Feedback Functions¶
Feedback functions, analogous to labeling functions, provide a programmatic method for generating evaluations on an application run. The TruLens implementation of feedback functions wrap a supported provider’s model, such as a relevance model or a sentiment classifier, that is repurposed to provide evaluations. Often, for the most flexibility, this model can be another LLM.
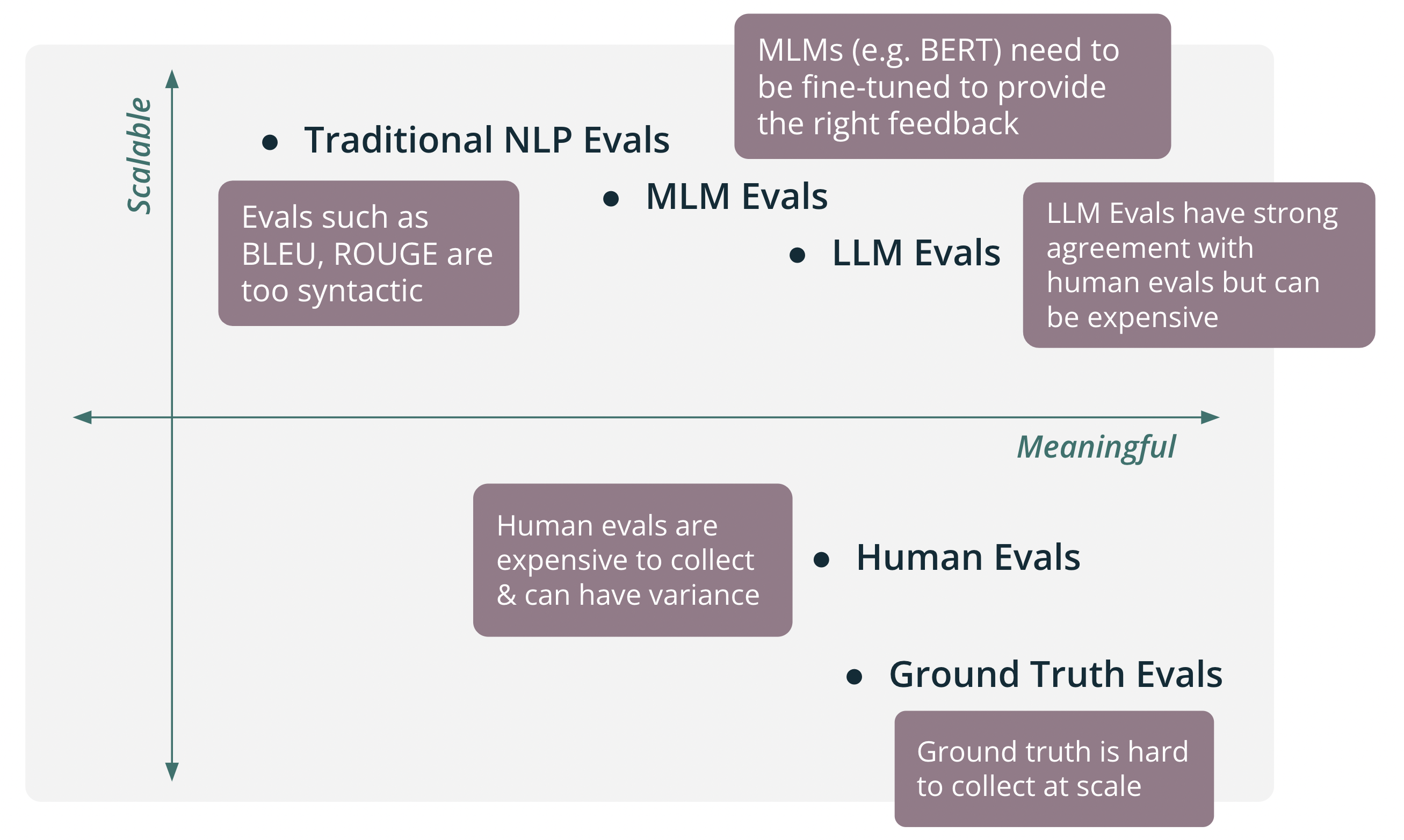
It can be useful to think of the range of evaluations on two axes: Scalable and Meaningful.
Domain Expert (Ground Truth) Evaluations¶
In early development stages, we recommend starting with domain expert evaluations. These evaluations are often completed by the developers themselves and represent the core use cases your app is expected to complete. This allows you to deeply understand the performance of your app, but lacks scale.
See this example notebook to learn how to run ground truth evaluations with TruLens.
User Feedback (Human) Evaluations¶
After you have completed early evaluations and have gained more confidence in your app, it is often useful to gather human feedback. This can often be in the form of binary (up/down) feedback provided by your users. This is slightly more scalable than ground truth evals, but struggles with variance and can still be expensive to collect.
See this example notebook to learn how to log human feedback with TruLens.
Traditional NLP Evaluations¶
Next, it is a common practice to try traditional NLP metrics for evaluations such as BLEU and ROUGE. While these evals are extremely scalable, they are often too syntactic and lack the ability to provide meaningful information on the performance of your app.
Medium Language Model Evaluations¶
Medium Language Models (like BERT) can be a sweet spot for LLM app evaluations at scale. This size of model is relatively cheap to run (scalable) and can also provide nuanced, meaningful feedback on your app. In some cases, these models need to be fine-tuned to provide the right feedback for your domain.
TruLens provides a number of feedback functions out of the box that rely on this style of model such as groundedness NLI, sentiment, language match, moderation and more.
Large Language Model Evaluations¶
Large Language Models can also provide meaningful and flexible feedback on LLM app performance. Often through simple prompting, LLM-based evaluations can provide meaningful evaluations that agree with humans at a very high rate. Additionally, they can be easily augmented with LLM-provided reasoning to justify high or low evaluation scores that are useful for debugging.
Depending on the size and nature of the LLM, these evaluations can be quite expensive at scale.
See this example notebook to learn how to run LLM-based evaluations with TruLens.